
What Does Above Par Mean? Above Par Definition Meaning Of Above Par Onlineslangdictionarycom
30 de enero de 2020What Is Bookkeeping? Definition, Objectives, Types And Methods
23 de abril de 2020Content

Companies with a healthy amount of https://www.bookstime.com/ can reflect positively in their ability to meet their short-term debt obligations. Another example of a company with tons of cash is Japanese video game company Nintendo, which has so much cash parked in its current assets ($5 billion) that even if it stopped selling products tomorrow, it could continue to pay its bills for years. Such securities and assets become important when a company has so much cash sitting around that it has no qualms about tying some of it up in slightly longer-term investment vehicles, such as bonds, that have maturities of less than one year. That allows the business to earn a higher interest rate than if it were to stick the cash in a corporate savings account. In addition to categorizing items on the classified balance sheet, companies prepare classified income statements, an example of which is shown below. In accounting terms, cash is the currency and coinage owned by a company.

Again, even though we say “cash,” we mean money that is available to spend right now or nearly right now. Marketable securities are fairly liquid, but not as liquid as cash equivalents because selling stocks and other marketable securities in a hurry may adversely affect the price . If you examine the above asset section of Facebook’s balance sheet, you may notice the assets are not listed alphabetically, or by descending amount, but by descending assessment of liquidity. You determine that prepaid rent, prepaid insurance, accounts receivable, and supplies are current assets but are not categorized as cash and cash equivalents. Summing the remaining balances, you solve for the cash and cash equivalents balance, which as you can see, turns out to be $4,500. Cash RatioCash Ratio is calculated by dividing the total cash and the cash equivalents of the company by total current liabilities. It indicates how quickly a business can pay off its short term liabilities using the non-current assets.
You Must Ccreate An Account To Continue Watching
The receipt is not subject to market conditions, nor can it be traded as a security. It is a good idea for investors to look at a business’s cash equivalents when deciding whether to invest in a company because this can give investors an idea of whether or not a company is likely to be able to pay its bills in the short term. Not all qualifying short-term, highly liquid investments are treated as cash equivalents. An agency discloses its policy for determining which items are treated as cash equivalents. Cash and Cash Equivalentsmeans all cash and any presently existing or hereafter arising deposit account balances, certificates of deposit or other financial instruments properly classified as cash equivalents under GAAP. Cash and cash equivalent are an important component of a balance sheet and resembles the financial health of a company. It can be used to pay off short term obligation very easily without any kind of borrowing needed.

In general, it is reporting the total in the current assets section of total assets. Similar to the manner in which cash and cash equivalents were examined in this chapter, the most important items reported on the classified balance sheet will be examined in later chapters. For example, Chapter 7 examines accounts receivable, while Chapter 9 examines property, plant, and equipment. GAAP allows this financial statement presentation because some investments are so liquid and risk adverse that they are considered cash. These investments are backed by the U.S. government and will always be paid.
What Are Cash And Cash Equivalents Cce?
Net working capital is equal to current assets, less current liabilities. The cash and cash equivalents line item on the balance sheet states the amount of cash on hand plus other highly liquid assets readily convertible into cash. The cash ratio—total cash and cash equivalents divided by current liabilities—measures a company’s ability to repay its short-term debt. Companies holding more than one currency can experience currency exchange risk.
- Furthermore, Cash and Cash Equivalents are also important factors for calculating numerous other ratios and calculations.
- Preferred stocks can be included within three months of the redemption date.
- A demand deposit is a type of account from which funds may be withdrawn at any time without having to notify the institution.
- A financial agreement offered by banks that provides a premium interest rate to clients who are willing to leave a lump-sum of cash in a savings account, untouched, for a defined period of time.
- Examples of demand deposit accounts include checking accounts and savings accounts.
Cash and cash equivalents information is sometimes used by analysts in comparison to a company’s current liabilities to estimate its ability to pay its bills in the short term. However, such an analysis may be excessively conservative if there are receivables that can be readily converted into cash within a few days; in this case, receivables should also be included in the analysis.
Whats Not Included In Cash Equivalents
Such a strongly capitalized business can take advantage of a tough financial climate to buy up competitors for a fraction of their true value. A decent amount of cash on hand gives management the ability to pay dividends and repurchase shares, but more importantly, it can provide extra wiggle room if the company runs into any financial difficulties. Erika Rasure, is the Founder of Crypto Goddess, the first learning community curated for women to learn how to invest their money—and themselves—in crypto, blockchain, and the future of finance and digital assets. She is a financial therapist and is globally-recognized as a leading personal finance and cryptocurrency subject matter expert and educator. Therefore, in the same manner, currency from foreign currencies is also considered as liquid and easily convertible assets.
- We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate.
- Adjusting Entries are used to adjust Financial Statements for transactions or other events that occur after the balance sheet date.
- Cash Equivalents are short-term highly liquid company assets that can be easily converted to cash and are not subject to any significant changes in value.
- Examples of cash equivalents include commercial paper, Treasury bills, and short-term government bonds with a maturity date of three months or less.
- Is a short-term debt instrument issued by a company that is guaranteed by a commercial bank.
- Similar to the manner in which cash and cash equivalents were examined in this chapter, the most important items reported on the classified balance sheet will be examined in later chapters.
In business handling, a lot of cash in foreign exchange may eventually lead to an exchange loss while converting it to the reporting currency. It can be used to repay the short-term obligations and other minor operating expenses as and when it is needed. When building a financial model, cash is typically the last item to be completed and will reveal whether or not the balance sheet balances and if the model is working properly. Banker’s AcceptanceBanker’s acceptance is a financial instrument guaranteed by the bank for the payments at a future date. The bank accepts the liability to pay the third party in case the account holder defaults.
Components Of Cash Equivalents
A payment guaranteed by a bank on behalf of the payer, bank drafts are considered guaranteed and immediately liquid upon execution. Just not money held in the reporting currency and held on the company’s account. When the Treasury issues these bonds to companies, the government is basically borrowing money from the company. However, investors must consider any political unrest, inflation, or other risks before making an investment in government bonds.
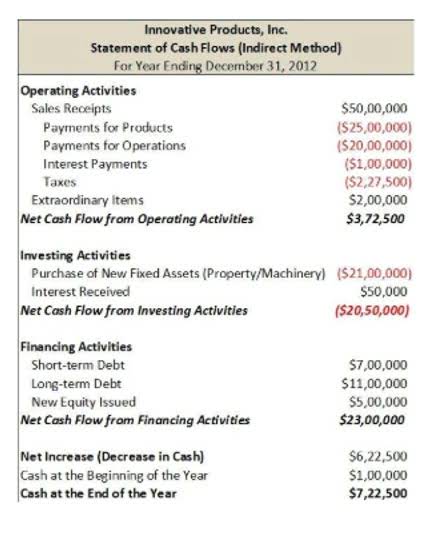
To reiterate, the “Cash and Cash Equivalents” line item refers to cash – the hard cash found in bank accounts – as well as cash-like investments. Net debt is a liquidity metric to determine how well a company can pay all of its debts if they were due immediately and shows how much cash would remain if all debts were paid off. Typically, a common stock investor is going to be happiest when the stock market heads down if she owns a large, profitable business with enormous cash reserves and little to no debt.
Cash Equivalents Examples
Examples of cash equivalents include commercial paper, Treasury bills, and short-term government bonds with a maturity date of three months or less. Marketable securities and money market holdings are considered cash equivalents because they are liquid and not subject to material fluctuations in value. This includes bills and coins, checks, money in checking accounts, and petty cash. Cash is the most liquid asset and is presented first on the balance sheet under the current asset section. Cash equivalents, similarly, have maturity dates of three months or less and include items that are quickly converted into a specified quantity of cash, such as money market accounts and commercial paper.
- Learn more about the standards we follow in producing Accurate, Unbiased and Researched Content in our editorial policy.
- That’s why management details each cash activity for the period on the statement of cash flows.
- Cash is necessary for buying and selling goods and services as well as paying debts.
- Based on the customer contract the manufacturer should put the deposit into separate bank account and not withdraw or use the money until the equipment is shipped and delivered.
- In this manner, cash flow statements detail the change in the business’s cash and cash equivalents from period to period and how these changes have arisen through its activities.
- Therefore very liquid securities are sometimes called cash equivalents.
It’s important to note that these investments are only considered equivalents if they are readily available and are not restricted by some agreement. For instance, if a company has a loan that requires it to maintain a minimum level of their treasure bills, these T-bills cannot be considered equivalents because they are restricted by the debt covenants. First, owners and investors can contribute money to the business in exchange for a percentage ownership in the company. Second, the company can generate money from selling goods or services to customers as part of its ongoing operations. Third, the business can borrow money from banks, financial institutions, and other lenders. Similar to a check, except the bank guarantees the availability of funds.
There are some exceptions to short-term assets and current assets being classified as cash and cash equivalents. This net change in cash and cash equivalents during the period plus cash and cash equivalent at the beginning of the period will get total cash and cash equivalent at the end of the period. The major categories reported on the classified income statement are revenues, operating expenses, other revenues and expenses, and income taxes expense. Operating expenses report resources used up by management in the major operation of the business. On the other hand, the other revenues and expenses section reports resources generated or used up by management in non-major operations of the business.
This cash is not available to the Group and must be held in ring-fenced accounts until released jointly by the Group and its advisors on the satisfaction of the complete terms of the merger. Or a note to account mentioning the same should be included in the notes of account. Equity InvestmentsEquity investment is the amount pooled in by the investors in the shares of the companies listed on the stock exchange for trading. The shareholders make gain from such holdings in the form of returns or increase in stock value. Consolidation can be done in this case because the drivers of the cash and investments roll-forward schedules are identical (i.e. the same net impact on the ending cash balance). Petty cash is a small amount of cash that is used for payment of insignificant expenses and the amount of it may vary depending on the organisation.
- Because money orders are immediately useable, they’re considered other cash.
- These are your most liquid assets, meaning they are cash, or can convert to cash, very quickly.
- As an example, consider cash balance in the 2014 balance sheet of Apple Inc.
- The property, plant, and equipment category on the classified balance sheet reports assets that have lives of many years and are used in the company’s operation.
- You probably won’t be able to tell if a company is weak based on its cash balance alone.
- Too much of cash may also resemble that company is not paying dividends to its shareholders and instead of retaining back the money.
Unlike to the current ratio, inventories and other assets that are difficult to convert into the cash are excluded from the calculation of quick ratio. A company with ample capital under its current assets is said to have a “fortress balance sheet.” One such example is Warren Buffet’s holding company, Berkshire Hathaway, which had a stockpile of more than $138 billion in cash by the end of 2020. The accumulation of cash from all of these activities will come up with the net change in cash and cash equivalents during the period. However, to declare cash equivalents as liquid assets, it also becomes essential to have the known market price for all these instruments. The main reason behind their position in the balance sheet is that they are current assets, and within current assets, they are mainly the most liquid amidst all the other short-term assets.
FundsNet requires Contributors, Writers and Authors to use Primary Sources to source and cite their work. These Sources include White Papers, Government Information & Data, Original Reporting and Interviews from Industry Experts. Learn more about the standards we follow in producing Accurate, Unbiased and Researched Content in our editorial policy.
The reason they’re considered “cash equivalents” is that in some cases the cash is not available while being pooled . “Money market” is a clever way of saying “highly liquid.” A money market fund, therefore, is investment in a fund that is highly liquid and considered a cash equivalent. Other cash receipts consist of money cash and cash equivalents owed to the company by a bank or other investment that are “due” in the present but currently have not been transferred. This may sound like a non-cash asset that’s highly liquid, but the difference is that this money is already under the company’s control — it just hasn’t been moved from one bank account to another.
Main Purposes Of Financial Statements Explained
Despite the clear distinction in the liquidity cycle, it is also rudimentary to realize that certain elements should also be accounted for when it comes to the items not necessarily included as cash or cash equivalents. In certain instances, there are situations where companies tend to be confused regarding the overall items which should be included in cash and cash equivalents and which should not be included. A business’s cash equivalents are shown at the top of the balance sheet and cash as these assets are the most liquid. Cash equivalents are short-term, highly liquid investments with a maturity date that was 3 months or less at the time of purchase. In other words, there is very little risk of collecting the full amount being reported. Also, if we look at Colgate’s short-term and long-term investments, they are pretty much nonexistent. So, most likely, we can deduct from the above that Colgate is not looking to pursue any major acquisition strategy.
Foreign Currency
Companies keep these for the purpose of meeting short-term cash commitments rather than for investment, or other purposes. Thus companies want a cash cushion to weather unexpected situations such as a shortfall in revenue, repair or replacement of machinery, or other unforeseen circumstances not in the budget.
